Physical Address
Arthur Avenue , BrookField , ILLINOIS , 60513 , United State
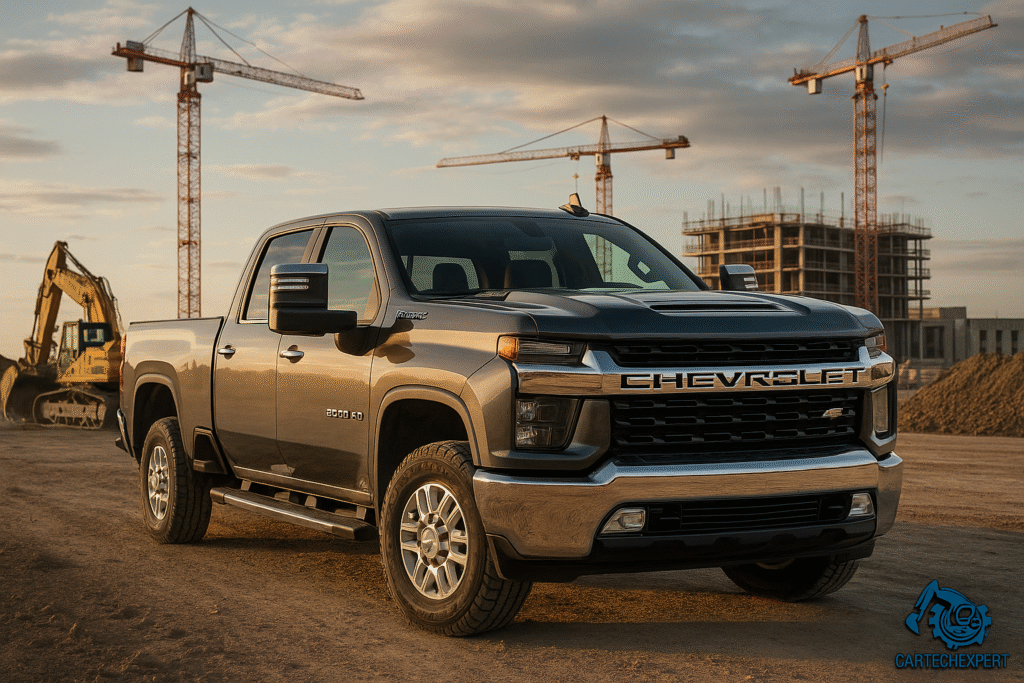
Anyone who has ever worked in a workshop, construction site, or fleet yard knows the feeling— the rumble of a V8 cold-start at dawn, the smell of diesel mixing with dust, the sense of trust you place in machines built to survive the worst conditions. For decades, Chevrolet and GMC trucks have been the backbone of technicians, engineers, and operators across the heavy equipment and automotive industries. This article explores how GM built two parallel brands that share engineering DNA yet serve different identities, needs, and professional cultures.
General Motors (GM) created a unique strategy early in the 20th century: two separate truck brands—Chevrolet and GMC—built on shared engineering platforms yet marketed to different customer segments.
GMC began producing trucks as early as 1911, focusing on commercial and industrial applications. Chevrolet joined the truck sector later with light-duty pickups designed for farmers and small transport operations.
The rise of highway systems and industrial expansion accelerated demand for durable trucks. GM introduced stronger frames, improved braking systems, and more reliable inline-six engines.
The C/K Series emerged, redefining the modern pickup. Both Chevrolet and GMC adopted V8 engines, stronger transmissions, and more advanced suspension designs.
Duramax engines, Allison transmissions, advanced towing systems, electronic diagnostics, and high-strength steel frames marked the rise of General Motors’ modern heavy-duty dominance.
Modern Chevrolet Silverado HD and GMC Sierra HD trucks incorporate cutting-edge systems:
Technicians and operators working with Chevrolet/GMC heavy-duty trucks must prioritize safety:
| Feature | Chevrolet Silverado | GMC Sierra |
|---|---|---|
| Brand Positioning | Consumer & general utility | Premium professional grade |
| Powertrain | Shared Duramax & Allison systems | |
| Exterior Design | Bold & rugged | Luxury-focused with chrome accents |
| Towing Capacity | Up to 36,000 lbs | Up to 36,000 lbs |
To target different customer groups: Chevrolet for general users and GMC for commercial, fleet, and premium markets.
Yes—engines, frames, and core components are shared. Differences lie in styling, trim level, materials, and target audience.
Both perform equally in terms of power and engineering. GMC offers more premium interior options, while Chevrolet provides a more rugged, value-driven configuration.
For more than a century, Chevrolet and GMC trucks have represented two sides of the same engineering powerhouse. Their evolution reflects GM’s commitment to durability, power, and innovation—serving technicians, engineers, and operators who depend on reliable machines every day.
Visit CarTechExpert.com for more in-depth technical guides, historical analyses, and maintenance resources for heavy equipment and automotive professionals.
Explore our store for diagnostic tools and professional equipment: store.cartechexpert.com
